
On this episode of We Talk Health, Kara Mobley interviews Dr. Jonathan Braun on Carotid Artery Disease and how it relates to stroke.
What exactly is carotid disease and how does it relate to stroke? Who can get it and how does it affect people? What options are there for treatment? All of these questions and more are answered.
To request an appointment with Dr. Braun, call Jackson Surgical Associates at 731-664-7395.
Podcast on Peripheral Artery Disease
Guest:
Dr. Jonathan Braun, MD, RPVI
Surgeon at JSA
Host:
Kara Mobley
Social Media Coordinator
Resources:
Carotid arteries take blood to the brain, face and neck. There are two carotid arteries, one on either side of the neck.
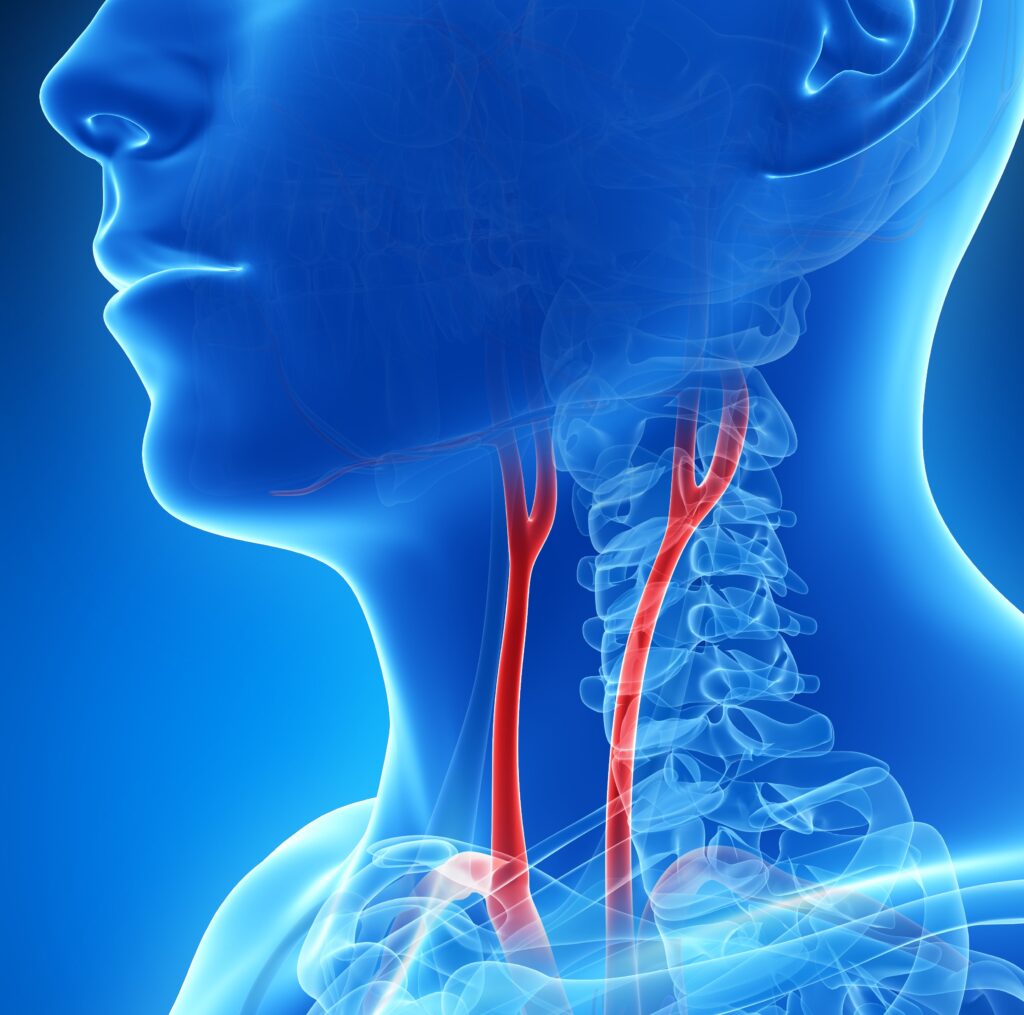
Carotid artery disease is a serious condition that occurs when the carotid arteries narrow, limiting oxygen delivery to the brain. This is commonly related to atherosclerosis, a build-up of plaque in the artery.
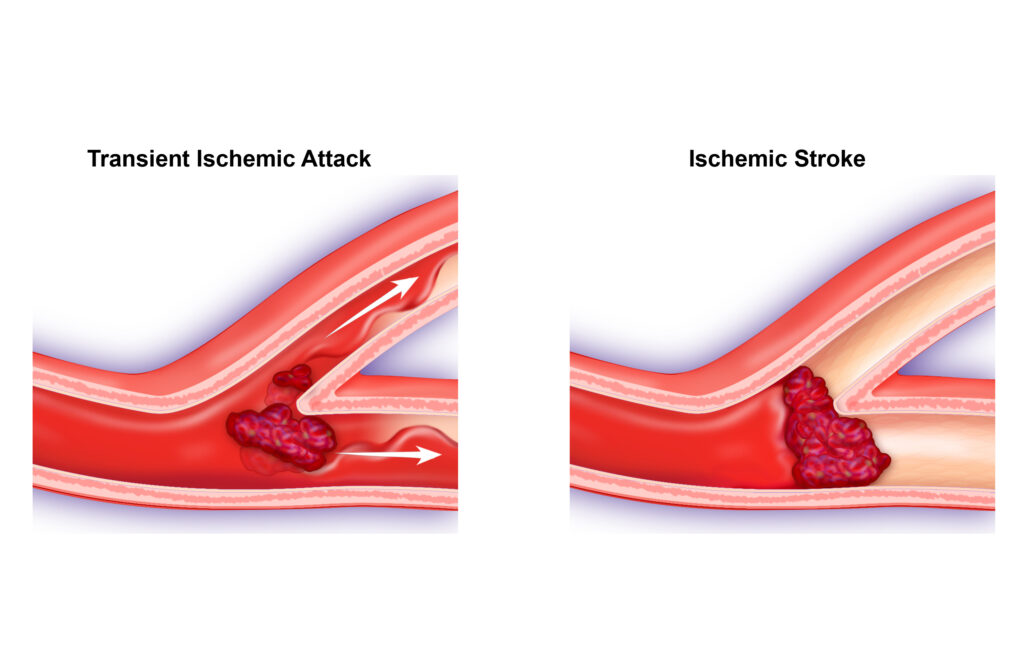
Plaque is comprised of cholesterol, calcium, fatty substances, and other materials found in the bloodstream. Plaque can slowly squeeze the artery closed, reducing blood flow. A clot that blocks the carotid artery, cutting off the blood supply to the brain and causing a stroke is known as occlusion.
Carotid artery disease can also cause a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or mini-stroke. A TIA occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops for a brief time. After a TIA, the blockage breaks up quickly and dissolves on its own. Most symptoms of a TIA disappear within an hour, although they may persist for up to 24 hours.
Many people don’t have symptoms of carotid artery disease in its early stages. It may be detected during an exam when the doctor may notice an atypical sound called a bruit when listening to your pulse. This faint whistling sound is a distinctive sign of a carotid artery blockage.
As carotid artery disease advances, the most common first sign may be a stroke or a TIA.
There are several risk factors for carotid artery disease that include diabetes, family history of stroke, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, high triglycerides, age, smoking, use of alcohol or drugs and neck trauma.
Treatments can include blood-thinning medications to help blood flow more easily and reduce the risk of clots. Carotid endarterectomy is a procedure that clears plaque from the carotid artery. Carotid angioplasty and stenting in which a small mesh tube (stent) is placed in the artery to hold it open, permitting healthy blood flow.
A stroke is a medical emergency and anyone who experiences the warning signs of a stroke should dial 911 immediately. Remember the acronym: BE FAST
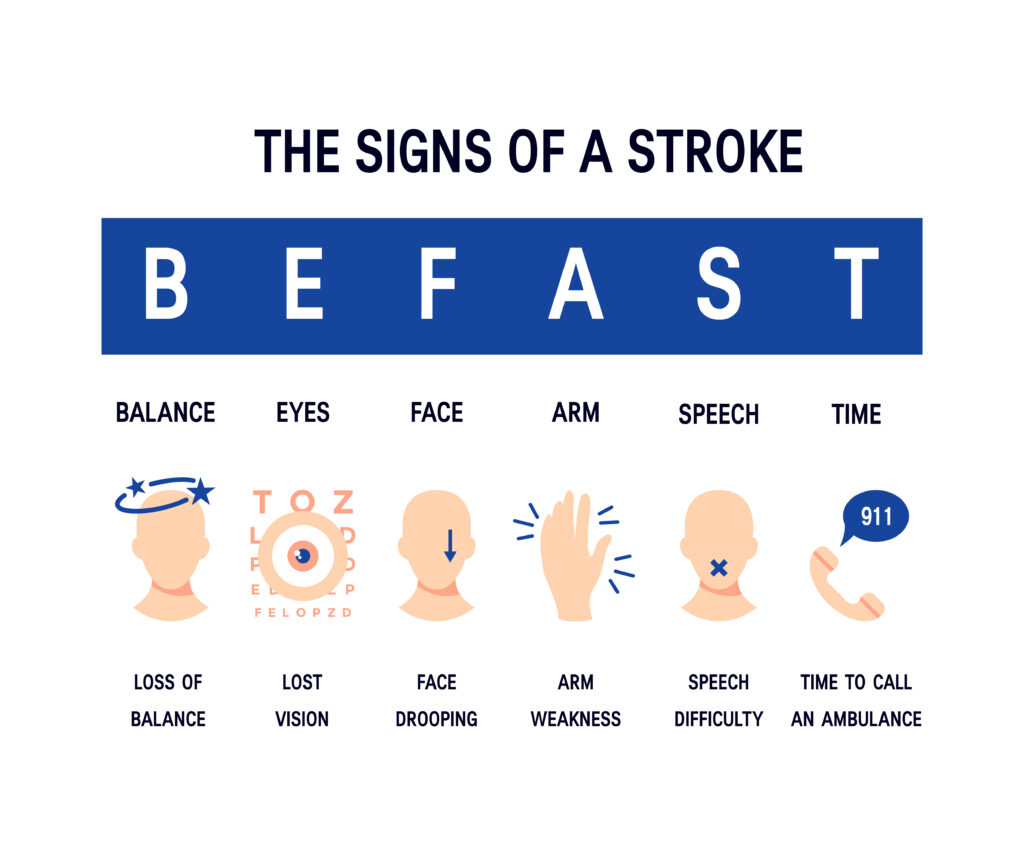
- Balance – Loss of balance
- Eyes – Lost vision
- Face – Face drooping
- Arm – Arm weakness
- Speech – Speech difficulty
- Time – Time to call 911
